For finance and accounting teams, the ability to anticipate future financial outcomes is not just a competitive advantage – it’s a necessity. And that’s what financial forecasting is for. Whether you’re a startup navigating growth or an established company refining your long-term strategy, accurate financial forecasts can guide critical planning and ensure alignment across teams. Here’s how.
What you’ll find in this article?
- What is financial forecasting?
- What are the common financial forecasting methods and models?
- What is financial forecasting process?
- Samples and examples of financial forecasts
- How can financial forecasting software help you streamline the process?
What Is Financial Forecasting?
Financial forecasting is the process of estimating or projecting a company’s future financial outcomes Based on historical data, current trends, and expected market conditions, this process aims to predict future revenues and business performance, giving the management teams valuable information they can use to improve budgeting process and overcome potential obstacles.
In the financial forecasting process, managers use past financial data, current trends and sales forecasting methodologies to predict key financial metrics, such as revenue, expenses, profits, and cash flow. This helps them to evaluate the potential financial performance of the entire company, strategic planning, budgeting, and investment decisions for a given period.
Due to the dynamic nature of today’s business environment, financial forecasting must be flexible and regularly updated to reflect recent changes or unforeseen external factors. Only with consistent updates can your cash flow forecasting remain accurate over the course of weeks and months.
Why Is Financial Forecasting Important?
Financial forecasting is essential for making informed business decisions. By predicting future cash flow, it helps organizations set realistic goals, allocate resources efficiently, and prepare for potential risks. Whether you’re planning for growth, managing day-to-day operations, or seeking investment, accurate forecasts provide a clear picture of what lies ahead—allowing leaders to stay proactive rather than reactive. It’s also a key tool for aligning teams around performance expectations and ensuring financial stability in both the short and long term.

Financial Forecasting Models
There are various forecasting methods that can help you assess future revenues and future costs. Still, none of those models are one-size-fits-all; the majority of them cater to the needs of just a fraction of companies with certain characteristics.
Quantitative Forecasting Methods
Want to create more accurate forecasts? Quantitative forecasting methods can definitely help you. These predictions are strongly rooted in historical data, allowing managers to precisely assess financial risk and mitigate it.
The most popular quantitative forecasting methods inlcude:
Linear regression
Linear regression uncovers the relationship between one or more independent variables (such as marketing spend, number of customers, or economic indicators) and a dependent variable (like revenue, expenses, or profit). By plotting historical data points and fitting a line of best fit, this method estimates how changes in inputs affect financial outcomes. It’s particularly powerful for detecting long-term trends and evaluating how key drivers impact your financial performance over time.
Moving average
The moving average method is ideal for identifying underlying trends by filtering out short-term fluctuations and random noise in the data. By averaging a set of past data points over a specified periods, it smooths out erratic variations and provides a clearer picture of consistent performance patterns. This technique is especially valuable for forecasting metrics that exhibit seasonal behavior or cyclical tendencies, such as retail sales, utility usage, or staffing needs.
Percent of sales
The percent of sales method is a straightforward yet effective forecasting tool, often used during the budgeting process. It assumes that certain expense categories, like cost of goods sold, marketing, or administrative costs, maintain a relatively stable ratio to sales. By projecting future sales and applying these fixed percentages, businesses can estimate future expenses and resource requirements.
Qualitative Forecasting Methods
If your company has little historical data or relies on the expertise of its employees, qualitative forecasting is definitely the right choice for you. This is a knowledge-based forecasting method that relies on experience of key stakeholders to create predictions and evaluate the risks.
There are two methods of qualitative forecasting that are commonly used across all industries:
Delphi method
The Delphi method gathers insights from a panel of experts through a series of questionnaires, typically conducted in multiple rounds. After each round, a facilitator summarizes the responses and provides feedback to the panel, allowing participants to refine their answers based on the group’s input. This iterative process continues until a consensus is reached.
The Delphi method is particularly useful for long-term forecasting or assessing the impact of disruptive changes where traditional data may not yet exist. It is also recommended for newly founded businesses with expert support on board.
Market research
Market research involves collecting and analyzing qualitative data directly from consumers, competitors, and other stakeholders to gain insights into future demand and trends. This can include techniques like focus groups, in-depth interviews, and surveys that explore attitudes, motivations, and buying behaviors. Market research is particularly valuable for launching new products, rebranding efforts, or expanding into unfamiliar markets where quantitative data may not be available or relevant.
Financial Forecasting Process – A Complete Guide
Collecting historical data over the last few months is not enough to make your financial planning accurate – only financial forecasting process can help you achieve that. Here’s how to approach financial modeling to create accurate forecasts and ensure your profits are more than satisfactory regardless of the circumstances.
Define Assumptions
To ensure that financial forecasting remains consistent, the first step of this process is to define its baseline and potential constraints. To do that, establish:
- The period your forecasts aims to describe – preferably months, quarters or years.
- The objective of forecasting the cash flow. Both negative and positive scenarios can help you achieve different results, from identifying risks to monitoring opportunities.
- The main revenue and expenditure categories and their possible fluctuations, for example related to demand forecasts, relevant economic conditions, or legal issues.
- The possible constraints, such as available resources or existing projects in planning production cycles.
Gather Information
To ensure the financial forecasts are as accurate forecasts, collect as many information on financial assets as you possibly can. That includes metrics such as:
- Revenue metrics, such as historical data on sales, conversion rates and customer acquisition rates, churn rates and seasonality patterns.
- Expense metrics, including fixed and variable costs, operating expenses (OPEX), cost of goods and services sold, capital expenditures, and depreciation.
- Cash flow metrics, namely: accounts receivable turnover and payable cycle, inventory turnover ratio, and cash burn rate (for startups and high-growth companies).
- Profitability metrics, such as gross profit, net profit and operating margins, project profitability rates, and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBIDTA).
- Business-specific metrics that generally depend on a particular industry. Those usually include: utilization rates, billable hours, headcount, and growth plans.
- Market and economy metrics, particularly inflation, interest rates and competitor’s performance, if such information is available.
Additionally, remember not to disregard the expert knowledge of managers and specialists directly involved in project execution in your company. Practical experience and hands-on approach of project managers, financial analysts and senior specialists might provide valuable insights on factors that might potentially impact the final financial statements.
Select Financial Forecasting Methods
Choosing the right forecasting method depends largely on three major factors:
- The nature and industry of your business
- The type of data available
- The specific goals of your forecast.
For short-term, tactical planning (for example, for forecasting revenue for the next quarter) quantitative methods are often most effective. These rely on historical revenue data patterns to project future outcomes and work best when trends are relatively stable and data is readily available. On the other hand, when forecasting in uncertain or rapidly changing environments, such as during a product launch or market disruption, qualitative methods may be more appropriate.
Often, the most reliable forecasts combine both approaches: using quantitative models for baseline projections, and overlaying them with qualitative insights to account for external variables or strategic shifts. Ultimately, the key is to align the forecasting method with your decision-making context and to remain flexible enough to update your approach as conditions evolve.
Conduct Financial Forecasting
While financial forecasting models might differ, they all have the same objective: to help managers predict future growth (or lack thereof) and anticipate challenges that might affect their income statement. To achieve that goal, combine your preferred financial forecasting methods with pre-defined constraints to create a range of forecasts – both positive and negative – describing the possible business performance for a chosen period.
To make the future spending and revenue even more accurate, remember to include consistent patterns and trends in your analysis. Conduct extensive market research, identify trends and business cycles and identify potential anomalies to expect the unexpected – and prepare for it.
Put the Forecasts to Work
Once your financial forecasts are complete, the next critical step is to apply them to real-world decision-making. Use your projections to guide budgeting, resource allocation, hiring plans, investment timing, and risk management strategies. Regularly compare actual performance against forecasted figures to identify variances, understand their causes, and adjust your assumptions or strategies accordingly.
Financial forecasts are not static; they should serve as living tools that evolve alongside your business. Schedule periodic reviews (monthly or quarterly) to update your models with fresh data and adjust for any internal or external shifts.
Turn Forecasts Into Precise Financial Decisions with BigTime
Business planning is never easy. Still, with only basic tools or, worse, Excel spreadsheets at hand, forecasting future expenses and revenue turns into a guessing game with no guarantee of success. With BigTime’s financial forecasting software, that changes.
How BigTime’s Financial Forecasting Tools Transform the Process?
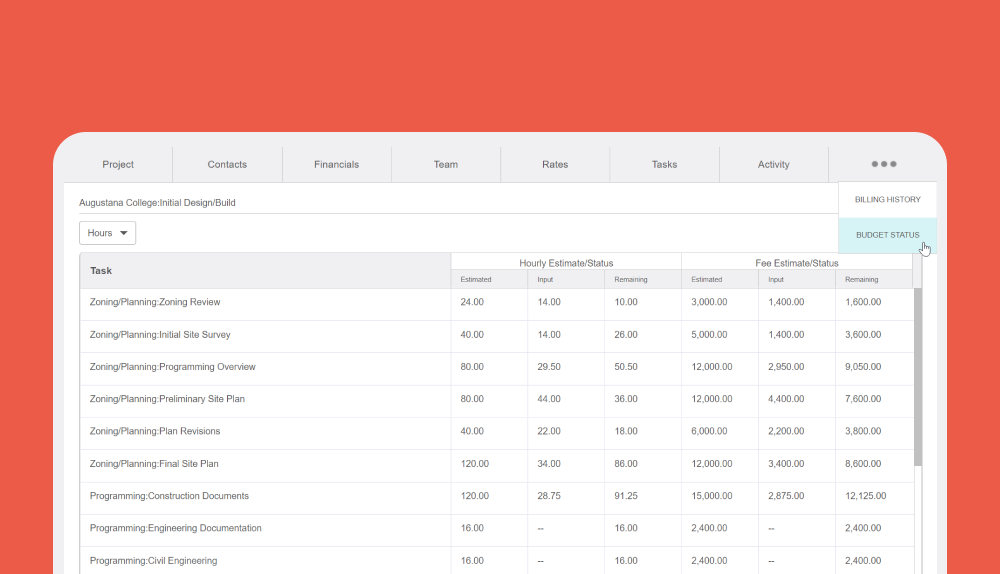
Financial forecasting tools in BigTime’s platform can help you:
- Allocate resources based not only on their skills and availability, but also wages and hourly rates – whatever you prefer.
- Monitor the use of project budget – it will be altered every time you create a new assignment or your employee fills in a new time log. Overheads included!
- Predict future income and test different financial scenarios for each project and for the entire company’s financial future.
- Create financial reports – our AI features will help you do that in seconds.
- Manage invoices you share with your customers, and their payments – our tool supports them, too.
In short: with BigTime, you have everything you need to monitor every penny in your organization.
Want to see how it works? Book a demo with BigTime or start a trial now to see how we can turn raw data into actionable insights.