In today’s fast-paced, project-driven world, knowing how your team’s time is spent isn’t just useful—it’s essential. Utilization rate is one of the most critical metrics for understanding productivity, profitability, and overall operational health.
In this article, we’ll break down what utilization rate is, why it matters, and how to calculate it accurately.
What’s in this article?
- What is utilization rate?
- What is the utilization rate formula?
- How to calculate utilization rates? Examples included!
- How to calculate team’s utilization rate?
- Utilization rate benchmark
What Is Utilization Rate? Definition
The utilization rate measures the percentage of an employee’s available working hours that are spent on work. It is a key performance indicator (KPI) used to track efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
As a project manager, you must have come to terms with the fact that the total working hours of an employee do not go all into creating a client’s desired output. In simple terms, the average utilization rate is the portion of an employee’s total working hours that is productive and is actively generating profits.
Importantly, just like in the case of classic utilization rate, billable utilization calculation does not account for overhead costs and it can only be used to monitor team members workload.
What is Billable Utilization?
Billable utilization is the percentage of an employee’s available working hours that are spent on billable client work. It is a key performance metric for professional services firms to assess efficiency, profitability, and workforce productivity.
For example, if one of team members spends 30 hours a week working for a paying customers, he has 30 total billable hours per week. The 10 hours he spends on non billable tasks, such as internal meetings or projects, are considered non billable work.
Why Monitoring Utilization Rate Is The Key To Your Desired Profit Margin?
If you are keen on tracking utilization and you proactively manage and try to achieve your target utilization rate, you might have a key to optimizing labor costs and boosting profitability in your company. Why? Because optimal utilization rates (preferably monitored in suitable project management tools) can help you:
Avoid bench time
If you don’t know how much you can deliver, you’re likely to end creating schedules below your desired optimal resource utilization. Lack of control in this area might contribute to a growing employee bench. And having your people spend too much time on the bench without earning a single penny might affect your billing efficiency and increase business costs. With healthy utilization rate, that doesn’t happen!
Clarify employee workload
When you know your team members’ utilization rate, you can make smarter and well-informed decisions for your company. For example, you could easily see the employees with too much non billable time and assess who could deal with a new project or work package in an existing project.
Identify staff shortage
If your development team is working at a 95%+ utilization rate and your QA team is operating at a 75% utilization rate, it means that your developers have a much higher workload than your QA specialists. Now that you know that, you can do something about it, like hire more developers and even out their average utilization.
Anticipate utilization problems
A software platform like BigTime Foresight allows not only for checking historical and tracking utilization rate on a daily basis, but also forecasting your utilization. By running utilization formula operations and checking this future utilization rate, you can quickly react – for example, hire additional resources or pass the info to the sales dept about resource availability so they can find projects for them. As a result, you can achieve your target profit margin faster!
Utilization Formula. How To Calculate The Capacity Utilization Rate?
Ideal utilization rate formula can be applied to both team members and the entire teams. While it does not account for administrative tasks that are included in non billable hours, it is a key metrics in determining team’s productivity and maintain profitability of the entire business.
Here’s how you can turn billable work from your time tracking software into employee utilization using a simple formula.
Formula for Utilization Rate:
On the face of it, billable utilization, also known as a utilization calculation or utilization rate, is a simple concept that measures how much time people are spending generating revenue. You take the hours that people are billable, divide by the hours they’re available and come up with a percentage using this billable utilization rate formula:

Where:
- Billable Hours = Time spent on work that can be invoiced to clients.
- Total Available Hours = Total working hours (typically excluding vacation, holidays, or sick days, depending on the company’s policy).
Calculating Utilization Rate – Example
Let’s take the example of a Management Consultant working at a consulting firm, XYZ Consulting Group. The company wants to measure their employee utilization to optimize their work and, as a result, make the most of resource costs incurred by the wages.
For the sake of this resource management example, we will assume that:
- The company operates on a 40-hour workweek.
- Employees are expected to work 2,080 hours per year (40 hours/week × 52 weeks).
- However, employees take vacation, holidays, and sick leave, so actual available hours for work may be lower.
In this example, we will calculate the monthly utilization rate for a single employee based on actual billable hours, taking into account holidays and time offs affecting the utilization rate in real-life examples.

Resource Utilization Rate Calculations
Let’s assume a consultant at XYZ Consulting Group works a standard month of 20 working days, with each day consisting of 8 hours, resulting in a total of 160 working hours for the month. However, during this particular month, the consultant took 2 personal days off and also had 1 public holiday, reducing their available working hours.
Since each workday consists of 8 hours, the 2 personal days off account for 16 lost working hours (2 days × 8 hours), and the public holiday accounts for another 8 lost working hours (1 day × 8 hours). This means the consultant’s total available working hours for the month are:
160−(16+8)=136 available hours
After determining the available hours, we now look at how the consultant allocated their time.
Out of the 136 available hours, they spent 100 total billable hours client work, while the remaining time was non billable time divided between internal meetings, internal tasks, training, and business development. Specifically, they recorded 20 hours for internal meetings and admin work, 10 hours for training and professional development, and 6 hours for business development, bringing the total logged hours to 136, which confirms accurate time tracking.
Now, we calculate utilization rate, which measures the percentage of available working hours spent on revenue-generating tasks. The formula for this is:

Substituting the values:
= (100/36)×100= 73.5%
This means that 73.5% of the consultant’s available time was dedicated to client work, which is within the expected range for professional services but slightly below an ideal target of 80-85% for many consulting firms.
To get a complete picture, we also calculate the overall utilization rate, which includes both billable and non-billable work. This is determined using the formula:

Since the consultant fully utilized their 136 available hours, the overall utilization rate is:
(136/136)×100=100%
This tells us that while the consultant used their entire available work time productively, only 73.5% was revenue-generating, with the rest going toward necessary but non-billable activities like internal meetings and professional development.
If the company’s target utilization is 80%, this consultant is slightly below that benchmark. To improve utilization, they might consider reducing time spent on administrative tasks, optimizing project assignments to increase billable work, or automating certain non-billable processes. However, a well-balanced workload is crucial, as excessive billable utilization can lead to burnout.
How to Calculate Team’s Utilization Rate – Example
At XYZ Consulting Group, a team of four consultants is working on client projects. The company follows a standard 20-working-day month, with each workday consisting of 8 hours, resulting in 160 total possible working hours per employee for the month.
However, actual billable hours vary by employee based on workload distribution. The billable hours for the four consultants this month are:
- Consultant A: 144 hours
- Consultant B: 120 hours
- Consultant C: 128 hours
- Consultant D: 152 hours
To calculate the team’s overall billable utilization rate, we first determine the total billable hours worked by all employees and compare it to the total available hours for the team. Since each consultant has 160 available hours, the team’s total available hours are:
160×4=640 available hours
Now, summing up the team’s billable hours:
144+120+128+152=544 billable hours
The team billable utilization rate is calculated using the formula:

Substituting the values:
(544/640)×100=85.0%
This means that the team achieved an 85% billable utilization rate, which is a strong number in the consulting industry, typically falling within the optimal range of 80-90%.
To further analyze the team’s performance, we can examine individual utilization rates, which were:
- For Consultant A: 90%
- For Consultant B: 75%
- For Consultant C: 80%
- For Consultant D: 95%
From this breakdown, Consultants A and D are operating at very high utilization levels (90% and 95%), which could be a sign of an intense workload, potentially leading to burnout if sustained long-term. Consultant B has the lowest utilization at 75%, which, while still reasonable, might indicate availability for additional project assignments.
If the firm’s target utilization is 80%, the team as a whole is exceeding expectations. However, to maintain balance, the firm may consider redistributing work from the highest-utilized consultants to those with lower utilization. Additionally, ensuring that non-billable work (such as internal meetings or business development) does not excessively reduce billable time will help optimize performance across the team.
Can Time Tracking Software Calculate Utilization?
BigTime Foresight certainly can!
As you can see in the example below, BigTime collects the information on all the billable hours, as well as the non billable work of your employees and automatically turns them into employee utilization report.
With such an information available in seconds, managers can not only track the target utilization rate, but also monitor billable rates, labor costs and improve their capacity planning with automated notifications. Finances are a part of this solution, too!
What Is a Good Employee Utilization Rate?
While a good utilization rate is often considered to be above 65%, and the perfect one – above 75%, there is not a single number that would fit all the industries.
The exact desired utilization rate depends on different factors – here are a few of them.
What Impacts The Optimal Utilization Rates?
Utilization rate for a given employee changes dynamically depending on a few different factors.
First is the seniority of the specialists in question. The range of responsibilities and assigned tasks changes with the person’s position – the higher position, the more organizational processes affect the resource utilization. Because of that:
- Interns and juniors are expected to spend around 90% of their total average labor hours on billable tasks. They also have the lowest billable rate and cost less to assign to projects,
- More experienced employees should have an employee utilization rate of over 80%,
- Senior employees, who usually participate in the organizational processes as experts, should spend around 60-70% of their time on development tasks,
- Managers, as they are mostly responsible for supervising the work, have an employee utilization rate of between 30-50% of their time.
- Executives rarely book their capacity at all; their range of responsibilities is simply too broad to be assigned to a single project.
Second is the industry. Companies in certain fields are simply more likely to monitor the time their employees spend on different tasks. For example, an average utilization rate in a production company is above 80%, while in architecture that value is closer to 60%. The difference is huge!
What if your utilization rate is 100%?
If you note a consistently high tracked utilization (the actual work logged by employees), it means that the team members spend all their time working on client projects.
This might mean that they’re overworked. Or that you’re not investing enough in their professional development or team-building.
In the long run, a 100% tracked utilization rate could pose a serious danger to your business and become a threat to profit margin due to the rising resource costs.
How To Improve Utilization Rate?
Calculating utilization rate is one thing; improving it is a very different story. Fortunately, there are a few simple tricks that will help you maximize that metric,
Is Non-Billable Utilization Your Enemy?
Not exactly. Before you jump right into optimizing utilization rates, you need to distinguish between two major metrics:
- Billable utilization, or the time spent on revenue-generating work.
- And productive utilization, that includes not only billable utilization, but also valuable non-billable activities.
Productive non-billable tasks still generate value, although it cannot be measured in dollars. Reducing such assignments might not only be unhelpful, but might also harm your business in the long run.
Strategically Increase Billable Workload
Having established which parts of non-billable utilization rates are really the problem, you might now proceed to reduce their duration. Look for opportunities to assign more billable tasks to underutilized employees. This might involve:
- Reassigning internal work to free up top performers
- Bringing in lower-cost or junior talent for support tasks
- Aligning team strengths to higher-value projects
- In the long-term perspective, acquiring new projects.
Predict the Future to Profit From It
In capacity management, following one’s gut feeling is not a way to go. To ensure that your plans are as close to reality as possible, use historical data and pipeline information to improve your forecasts. This helps reduce “bench time” (idle capacity) and avoid overcommitment.
Eliminate Time Leakage
This meeting could have been an email… And it should have been! Eliminating similar time-consuming and non-essential time drains is one of the simplest methods for improving utilization rates.
By reducing:
- Excessive admin work
- Meetings without clear outcomes
- Poor task prioritization
Your employees might find much more time for activities that actually generate profit. Encourage time-blocking and clear workflows to keep time focused on high-value work.
Balance Workload Across the Team
Is that one senior employee way too busy again? Change that! Avoid burnout in high-performers and underutilization in others to prevent employee burnout and control turnover rates. Regularly review capacity reports to redistribute assignments and ensure workload equity.
Review and Optimize Utilization Rates
Utilization isn’t “set and forget.” Use weekly or monthly reviews to track trends, spot inefficiencies, and adjust team assignments as needed.
Tracking Utilization Rate Starts Here
To sum it all up, a fairly simple notion of determining how busy people are is more nuanced than meets the eye, depending on what the organization is looking to accomplish. It might also be the key to optimal billing rate and improved resource costs – or, at least, the optimal use of resources.
Firms should consciously and deliberately decide which assumptions and approaches to use and understand what behaviors those decisions are likely to drive. Everyone who is responsible for measuring and optimizing resource utilization rates needs to understand the assumptions and ensure that the approaches are used consistently with their intent.
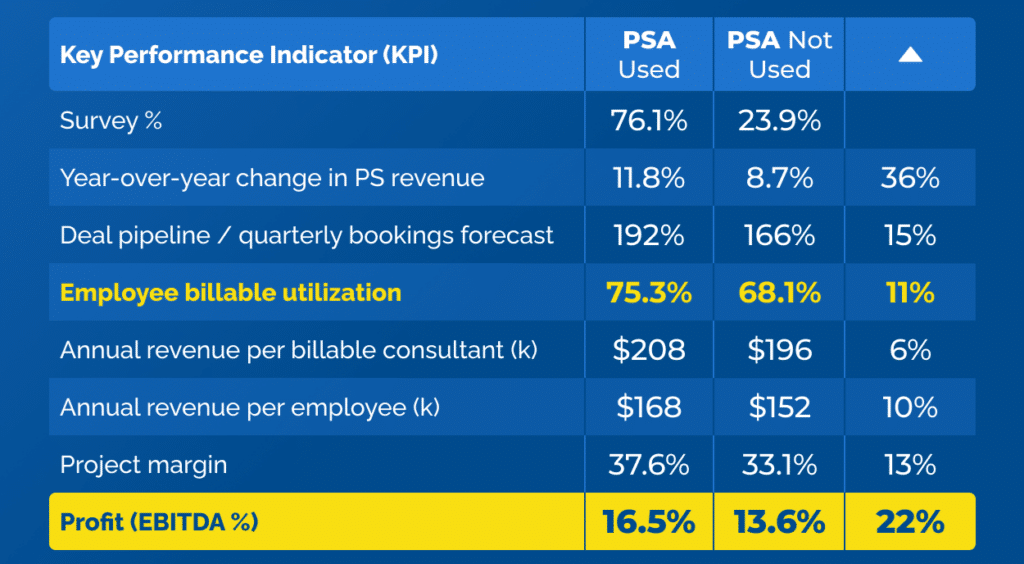
One of the most important aspects of measuring and managing utilization is being able to do it easily and consistently. Professional Services Automation (PSA) Software can help consulting firms do this, resulting in a higher utilization rate of 7 percentage points. This translates into improved billable utilization of nearly a whole month per billable employee per year.
To learn more about these other metrics, download our white paper, Metrics that Matter for Professional Services, or read more about billable utilization in our post about how optimal resource utilization can fuel growth. And don’t forget to download the SPI Research for benchmarking targets.
The price for poor resource allocation and management and utilization rate is getting costlier for businesses by the day, from hiring costs to clients dissatisfaction and contract termination. BigTime allows project managers to handle communication, resource management, and invoicing financials within the same comprehensive platform. Request a demo to learn more today!